.png)

.png)
.png)


-
.png) 0086-757-85407388
0086-757-85407388 -

-
 terrychen@wintoly.com
terrychen@wintoly.com


.png)

.png)
.png)


.png)




Discover the intricacies of powder coating, its manufacturing process, and the essential quality controls that ensure a successful finish.
This comprehensive guide walks you through the journey of becoming well-versed in the realm of powder coating.
Powder coating is a unique type of coating that's applied as a free-flowing, dry powder. Unlike traditional liquid paint, which is delivered via an evaporating solvent, powder coating is typically applied electrostatically and then cured under heat or with ultraviolet light. This results in a hard, durable coating that is much tougher than conventional paint.
Primarily used for coating of metals, such as household appliances, aluminum extrusions, drum hardware, and automobile and bicycle parts, powder coating has gained popularity due to its flexibility, environmental friendliness, and ability to deliver a range of finishes.
As a leading powder coating manufacturer, we provide a wide array of colors and finishes that resist chipping, scratching, fading, and wearing than other finishes. Our powder coating offers an attractive, durable, and high-quality finish that not only enhances the look of products but also improves their lifespan and functionality.
Powder coating plays an integral role across a wide spectrum of industries. Its unique properties make it an ideal choice for businesses seeking durable, high-quality, and environmentally-friendly finishes.
In the automotive industry, powder coating is used extensively for its resilience and durability. It's used in various car parts including wheels, bumpers, grills, door handles, and radiators, providing long-lasting protection against corrosion, heat, impact, and extreme weather conditions.
In construction and architecture, powder coating is used for coating aluminum extrusions for windows and doors. It's also used on railings, pipelines, roofing materials, and building facades, providing them with an attractive finish that's resistant to environmental effects.
Most home appliances, such as refrigerators, washing machines, dryers, and microwaves, benefit from powder coating. It provides a durable, scratch-resistant finish that can withstand frequent handling and cleaning.
As a powder coating manufacturer, we work closely with businesses across these industries to provide solutions that enhance the functionality, aesthetics, and longevity of their products.

As we've already discussed, powder coating is a free-flowing, dry powder that is applied electrostatically and then cured under heat or ultraviolet light. Now, let's explore why powder coating has become a preferred choice over traditional liquid coatings in many industries.
Powder coating provides a more durable finish than liquid paints can offer, while still providing an attractive finish. Powder coated products are more resistant to diminished coating quality as a result of impact, moisture, chemicals, ultraviolet light, and other extreme weather conditions.
Powder coating is also highly protective of our environment. While liquid finishes contain solvents which have pollutants known as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), powder coating contains no solvents and releases negligible amounts, if any, VOC into the atmosphere. Thus, there is no need for finishers to buy costly pollution control equipment.
From an economic perspective, powder coating has many advantages over liquid coating. The powder coating process involves fewer steps than the liquid coating process, which can save time and therefore reduce labor costs. Additionally, powder coating can cover larger areas with less material than liquid coating, making it more efficient.
As a leading powder coating manufacturer, we consistently provide high-quality, durable, and environmentally-friendly powder coating solutions that meet the needs of various industries.
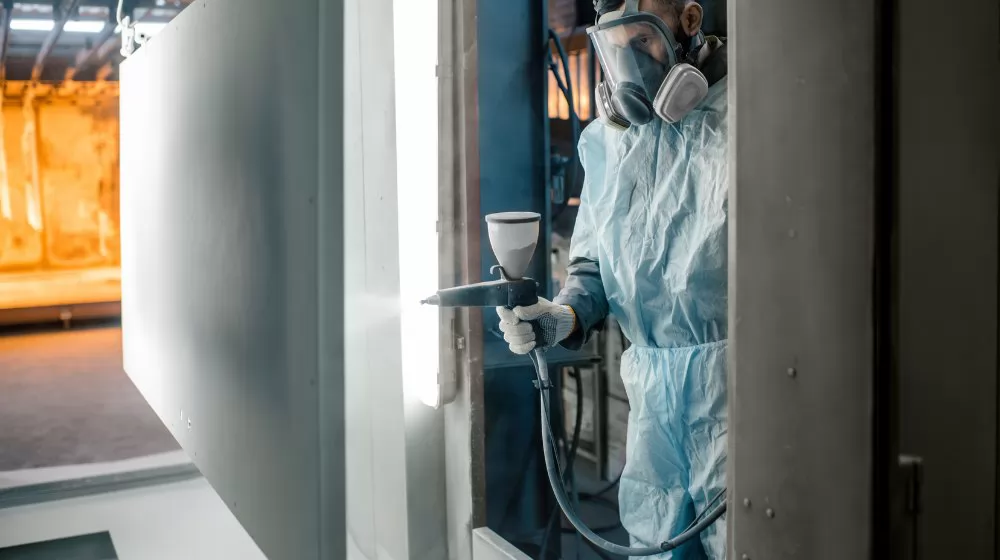
The powder coating process involves several key steps, including surface preparation, application, and curing. Understanding these steps helps explain why powder coating produces a superior, durable finish.
Before the application of the powder coating, the surface of the product to be coated must be properly prepared. This involves cleaning the surface to remove any dirt, grease, or rust that could hinder the adhesion of the powder coating. Techniques like sandblasting, stripping, and chemical washing are often used in this stage.
There are several methods of applying the powder coating, but the most common is the electrostatic spray method. This involves charging the powder particles and spraying them onto the surface, where they are held in place by an electrostatic charge until curing.
The fluidized bed method involves heating the part and then dipping it in a tank of fluidized powder. The powder sticks to the hot part, where it melts and fuses into a hard, protective coating.
Once the powder is applied, it needs to be cured to form a hard, durable coating. This is typically done using heat, which causes the powder to melt, flow, and then harden into a tough, protective layer. Some types of powder can also be cured using ultraviolet light or chemicals.
As a powder coating manufacturer, we utilize these techniques and processes to provide top-tier, durable, and attractive powder coating finishes for a variety of applications.

Thermosetting powder coatings are a type of powder coating that undergoes an irreversible chemical reaction during the curing process. This reaction enhances the performance properties of the coating. Thermosetting powder coatings are known for their superior durability, resistance to heat, and excellent finish.
Thermosetting powder coatings are commonly used in the automotive industry, outdoor furniture, home appliances, and many other products that require a highly durable finish. The benefits include excellent durability, corrosion resistance, high-temperature stability, and the ability to provide a wide range of finishes and colors.
Examples of thermosetting powder coatings include epoxy, polyester, and acrylic powders. Epoxy powder coatings are known for their excellent chemical and corrosion resistance. Polyester powder coatings are known for their excellent outdoor durability and UV resistance. Acrylic powder coatings are known for their excellent clarity, gloss, and UV resistance.
Thermoplastic powder coatings are a different type of powder coating that can soften when heated and harden when cooled. This process is reversible and can be repeated, which provides the advantage of being able to repair any coating damage by simply reheating the surface.
Thermoplastic powder coatings are often used in applications that require a flexible, impact-resistant coating. They're commonly found on items such as wire racks, outdoor furniture, and medical equipment. The benefits of thermoplastic coatings include their excellent impact resistance, flexibility, and chemical resistance. Additionally, they can be recycled and are environmentally friendly.
Examples of thermoplastic powder coatings include nylon, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polyolefin. Nylon powder coatings are known for their excellent impact resistance and flexibility. PVC powder coatings are known for their chemical resistance and electrical insulation properties. Polyolefin powder coatings are known for their excellent adhesion and flexibility.
Hybrid powder coatings, as the name suggests, are a blend of two or more types of powder coating materials, typically a combination of epoxy and polyester. They're designed to offer the best of both worlds, combining the durability and chemical resistance of epoxy with the UV resistance and flexibility of polyester.
Hybrid powder coatings are typically used in indoor applications where UV resistance is not as critical. They're often found on items such as office furniture, shelving, and light fixtures. The benefits of hybrid coatings include their excellent chemical resistance, smooth finish, and lower cost compared to pure epoxy or polyester coatings.
The most common type of hybrid powder coating is the epoxy-polyester hybrid, known for its good flow properties and over-bake resistance. It offers a good balance between the excellent performance properties of epoxy and the outdoor durability of polyester.
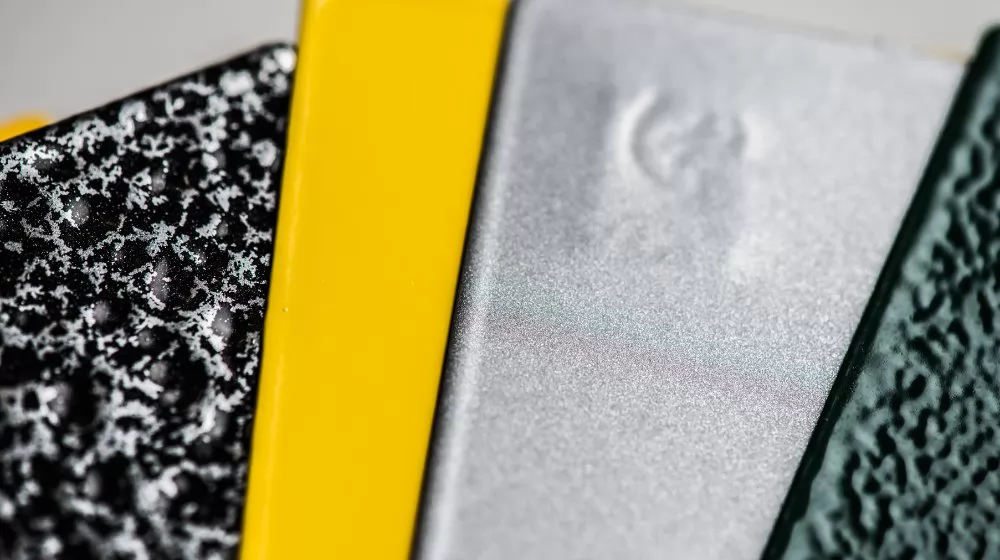
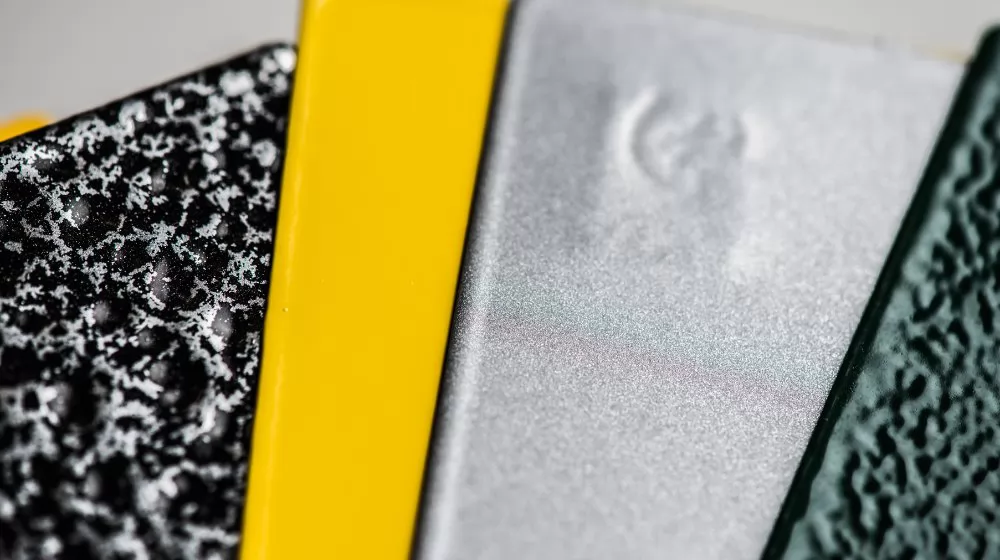
There's a broad spectrum of powder coating finishes available, each with unique aesthetics and applications. Let's delve into some of the distinctive finishes that can be achieved with powder coating.
Smooth powder coating offers a sleek, seamless finish that is often used for automotive parts, appliances, and furniture. The high-gloss variant provides a shiny, reflective surface, while the matte variant gives a subdued, non-reflective finish.
Wrinkle powder coating creates a textured finish that resembles a series of small wrinkles or ripples across the surface. This finish is excellent for hiding surface imperfections and providing a grip-enhanced surface, making it a popular choice for tools, equipment, and certain types of furniture.
Sandy powder coating produces a fine-grained, sand-like texture. This robust and durable finish is often used for outdoor furniture, industrial equipment, and other items that require added resistance to wear and tear.
Antique powder coating provides a unique, aged finish that mimics the appearance of weathered or oxidized metal. It's commonly used for decorative items, architectural features, and other applications where an "old-world" aesthetic is desired.
Metallic powder coating incorporates metallic flakes into the coating to achieve a sparkling, metallic finish. It's a popular choice for automotive parts, decorative items, and any application where a flashy, eye-catching look is desired.
Wood Effect Powder Coating allows for a realistic wood grain finish on metal surfaces. It is extensively used in applications like furniture, doors, and architectural details where a natural wood aesthetic is desired but the strength of metal is required.
These are just a few examples of the myriad of finishes that can be achieved with powder coating. Each type offers unique aesthetic and functional advantages, allowing manufacturers to tailor the finish to the specific needs of the application.

Powder coating materials are diverse, each with their distinct features, advantages, and limitations. They cater to various industries due to their unique properties. Let's delve into some of the most common powder coating materials.
Polyester is known for its excellent weather resistance, good mechanical properties, and vibrant color choices. However, it might lack chemical resistance compared to other materials. This type of powder coating is commonly used in outdoor furniture, automotive parts, and architectural applications.
Epoxy offers superior chemical resistance, excellent mechanical performance, and good adhesion. Its main limitation is poor UV resistance, which can lead to color changes when exposed to sunlight. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery often use epoxy powder coating for its durability.
Polyurethane powder coating is known for its exceptional weather resistance, good chemical resistance, and excellent flexibility. However, it may be more expensive than other types of powder coatings. It finds applications in outdoor furniture, automotive parts, and other outdoor applications.
Acrylic powder coating is recognized for its excellent weatherability, high gloss potential, and good color retention. Its limitation is its lower chemical and impact resistance compared to other materials. This type of coating is often used for automotive trim, wheels, and other parts where a glossy, durable finish is desired.
When it comes to powder coating, proper surface preparation is of utmost importance. It’s a critical precursor that significantly influences the adhesion, durability, and finish of the powder coating. Let's discuss this in more detail.
Before applying the powder coating, it’s vital to thoroughly clean and prepare the surface. This ensures that the coating adheres properly and provides a smooth, uniform finish. Poor preparation can lead to issues such as uneven coating, poor adhesion, and reduced lifespan of the coating.
There are various methods to clean and prepare the surface for powder coating. The choice of method depends on the type of surface and the level of cleanliness required.
Solvent Cleaning: This method uses solvents to remove grease, oil, and other contaminants. It’s typically used for smaller items or for surfaces that are not heavily soiled.
Abrasive Blasting: This technique uses pressurized air or water to propel abrasive materials against the surface. It’s effective for removing rust, scale, and old coatings, providing a rough surface ideal for powder coating adhesion.
Chemical Pretreatment: Involves the use of chemicals to clean and etch the surface. This method is often used for surfaces that are heavily soiled or have intricate shapes that are hard to clean with other methods.
After the surface has been cleaned and prepared, it’s important to inspect and evaluate it before applying the powder coating. This involves checking for any remaining contaminants or imperfections that could affect the quality of the coating. Proper inspection ensures a high-quality, long-lasting finish.

Powder coating has many advantages over traditional liquid coatings, which have made it a popular choice in various industries. Let's delve into some of these advantages.
One of the major advantages of powder coating is its durability. It is resistant to corrosion, chipping, and scratching. Powder coatings also provide excellent protection against harsh UV radiation, helping to maintain the color and gloss of the coated object for longer periods. In addition, they offer superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals, enhancing their durability in challenging environments.
Powder coating is an environmentally friendly process. Unlike traditional liquid coatings, it does not contain harmful solvents or release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere. The powder coating process also allows for nearly 100% material usage, reducing waste and making it an efficient and sustainable choice.
Finally, powder coating is cost-effective. While the initial costs may be higher than liquid coatings, the long-term savings are substantial. Powder coatings require less maintenance and have a longer lifespan, reducing the need for reapplications. The efficiency of the coating process and the absence of VOC emissions can also save costs associated with waste management and regulatory compliance.
The application process is key to the success of a powder coating job. The right application technique ensures even distribution of the powder, good adhesion, and a smooth finish. Let's discuss some of these techniques in more detail.
The electrostatic spray method involves charging the powder particles and spraying them onto the grounded workpiece. The charged particles are attracted to the workpiece, ensuring they stick evenly to the surface. The coated workpiece is then heated in an oven to melt the powder and form a hard, durable coating.
The equipment used in electrostatic spray coating includes a powder feeding system, an electrostatic spray gun, and a curing oven. The powder feeding system feeds the powder to the spray gun, where it is electrostatically charged. The spray gun then disperses the charged powder onto the workpiece. The coated workpiece is cured in the oven, where the powder melts, flows, and hardens to form the coating.
Electrostatic spray coating is highly efficient and provides a uniform, durable coating. It allows for quick color changes and is suitable for coating complex shapes. However, it may not be suitable for very thick coatings or for coating parts with deep recesses, as the charged particles may not penetrate deeply enough.
Fluidized bed coating involves preheating the workpiece and dipping it into a bed of fluidized powder. The heat from the workpiece causes the powder to melt and adhere to the surface, forming a coating. The workpiece is then further heated in an oven to fully cure the coating.
The main equipment used in fluidized bed coating includes a fluidized bed and a curing oven. The fluidized bed contains the powder, which is aerated to give it a fluid-like behavior. The preheated workpiece is dipped into the fluidized bed, and the powder adheres to the surface. The workpiece is then placed in the oven to cure the coating.
Fluidized bed coating allows for thick, uniform coatings and is ideal for coating small parts in bulk. However, it requires precise control of the preheat temperature, and it's not suitable for parts with complex shapes or internal cavities.
Electrophoretic deposition (EDP) is a process where charged particles in a liquid medium migrate under the influence of an electric field and deposit on an electrode. In powder coating, the workpiece serves as the electrode, and the coating forms when the powder particles deposit on the workpiece.
In EDP, the equipment typically includes a tank filled with a liquid medium containing the powder, an electrode setup, and a power supply to generate the electric field. The workpiece is immersed in the liquid medium, and an electric field is applied. The charged particles migrate towards the workpiece and deposit on its surface, forming the coating. The workpiece is then cured in an oven.
EDP allows for the uniform coating of complex shapes and the coating of internal surfaces, which can be a challenge for other methods. It also provides excellent corrosion resistance. However, it can be a more expensive process due to the costs of the liquid medium and waste disposal.

Heat curing is a process in which the powder-coated workpiece is heated in an oven. The heat causes the powder to melt, flow, and chemically react to form a hard, durable film. This process is the most common method of curing in powder coating.
The types of ovens used for heat curing include convection ovens, infrared ovens, and combination ovens. Convection ovens heat the air around the workpiece, while infrared ovens use electromagnetic radiation to heat the workpiece directly. Combination ovens use both methods. Curing temperatures can range from 350 to 400 degrees Fahrenheit, depending on the specific type of powder used.
Heat curing provides a strong, durable finish that is resistant to weathering, chemicals, and UV light. However, it requires energy-intensive equipment and may not be suitable for temperature-sensitive substrates.
UV light curing, also known as ultraviolet curing, is a process in which ultraviolet light is used to initiate a chemical reaction that hardens or cures a coating. The coating material contains special photoinitiators that absorb UV light and convert it into chemical energy to trigger the curing process.
UV curing systems typically consist of a UV light source, a conveyor system to transport the workpiece, and a control system. The UV light source emits a high intensity UV light, which is absorbed by the photoinitiators in the coating, causing them to decompose and initiate the polymerization process. This results in a cured, hardened film on the surface of the workpiece.
UV light curing offers the advantage of rapid curing times, often in a matter of seconds, which can increase productivity. It also provides a high-quality finish with excellent scratch and solvent resistance. However, it is generally more expensive than other curing methods and may not be suitable for thick coatings or substrates with complex shapes, as the UV light may not reach all areas effectively.
Chemical curing is a process where a chemical reaction is initiated by a curing agent, also known as a hardener, which is mixed with the coating material. The curing agent reacts with the coating material to form a cross-linked, hardened film.
There are various types of chemical curing agents, including amines, polyamides, and isocyanates. The choice of curing agent depends on the specific requirements of the coating, such as the desired curing speed, film properties, and environmental conditions.
Chemical curing allows for a high degree of control over the curing process and can produce coatings with excellent hardness, chemical resistance, and durability. However, it requires careful handling and mixing of the curing agent and coating material, and the curing process may be sensitive to temperature and humidity conditions.
In the world of powder coating manufacturing, quality control plays a pivotal role in ensuring successful and durable coatings. It is the cornerstone that ensures the output meets the predefined standards and the customer's expectations.
Quality control ensures the longevity and durability of the powder coating, impacting the overall aesthetics and protection the coating provides. It minimizes the risk of coating failures such as poor adhesion, color variance, and premature coating degradation.
There are several standards and certifications that guide the quality control process in powder coating. These include ISO 9001, which is related to quality management, and ISO 45001, focused on occupational health and safety. Certifications such as Qualicoat and GSB International are also crucial in the industry, signifying adherence to stringent quality requirements.
In the world of finishes, powder coating stands out for its durability, cost-effectiveness, and environmentally friendly properties. As one of the leading powder coating manufacturers in China, Wintoly is committed to providing superior powder coating solutions and custom coating services, ensuring a high-quality finish for various applications. Visit our website to explore our range of services and products, and discover how we can transform your products with our advanced powder coating solutions.

 terrychen@wintoly.com
terrychen@wintoly.com
.png) 0086-757-85407388
0086-757-85407388
 6 Chaoyang Rd., National Demonstration Eco-industrialzone, Nanhai, Foshan,Guangdong,China
6 Chaoyang Rd., National Demonstration Eco-industrialzone, Nanhai, Foshan,Guangdong,China

.png)
