.png)

.png)
.png)


-
.png) 0086-757-85407388
0086-757-85407388 -

-
 terrychen@wintoly.com
terrychen@wintoly.com


.png)

.png)
.png)


.png)




Table of contents:
Powder coating and epoxy coating are two distinct methods employed in the finishing industry, each offering unique characteristics and applications. Understanding the differences between these coatings is essential for making informed decisions in various industries and applications. In this comparison, we will explore the key distinctions between powder coating and epoxy coating, shedding light on their composition, application processes, advantages, and suitable use cases.
Coatings play a pivotal role in enhancing the performance and longevity of various surfaces and materials. Understanding the importance of coating is essential for making informed decisions when choosing between different options such as powder coating and epoxy coating.
Coatings serve several critical functions, including protection against corrosion, wear and tear, and environmental elements. They act as a barrier, shielding surfaces from factors that can compromise their integrity. Additionally, coatings can enhance aesthetics, providing a visually appealing finish that aligns with the intended purpose and design.
As we delve into the comparison between powder coating and epoxy coating, it's crucial to keep in mind the overarching significance of coatings in preserving and enhancing the functionality of diverse materials.
Powder coating is a popular and effective method of applying a protective and decorative finish to a variety of surfaces. Unlike traditional liquid paint, powder coating involves the application of a dry powder made up of finely ground particles of pigment and resin. The process starts with the electrostatic application of the powder onto the object or surface, which is typically grounded. This electrostatic charge causes the powder to adhere to the surface, creating a uniform and consistent coating.
Once applied, the coated object is then cured in an oven where the powder particles melt and fuse to form a durable and smooth finish. The curing process not only enhances the adhesion of the coating but also results in a chemical reaction that produces a tough, resilient surface.
One of the key advantages of powder coating is its ability to create a seamless and even finish without the drips, runs, or sags commonly associated with traditional liquid paint. Additionally, powder coatings are available in a wide range of colors and textures, offering versatility in design and aesthetics. This method is commonly used in various industries, including automotive, furniture, appliances, and architectural applications, due to its durability and resistance to chipping, scratching, and fading.
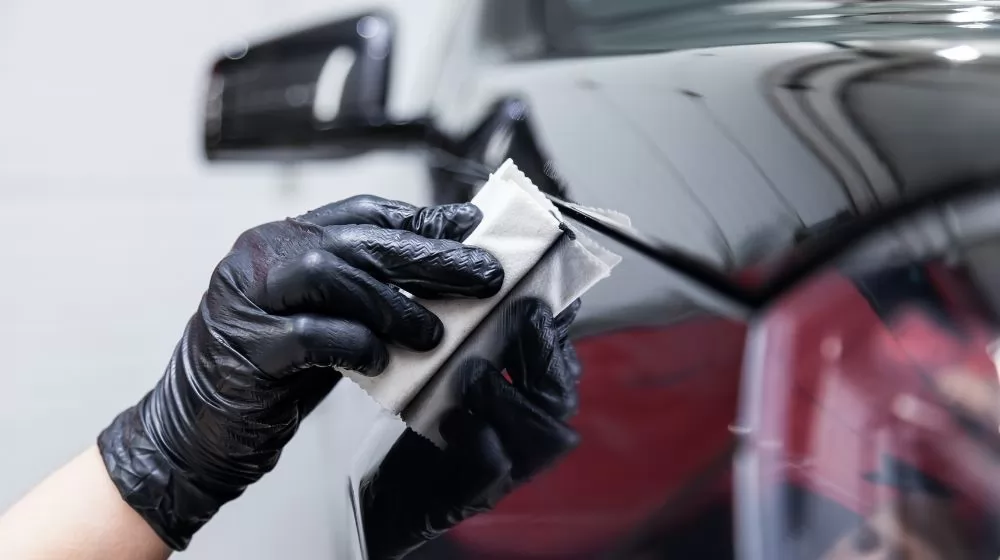

Durability: One of the primary advantages of powder coating is its exceptional durability. The cured finish is resistant to scratches, chips, and other forms of wear and tear. This durability makes powder-coated surfaces ideal for applications in high-traffic areas or environments where the coated objects may be subjected to harsh conditions.
Enhanced Aesthetics: Powder coating provides a smooth, even finish with a wide range of color options. This versatility allows for the creation of visually appealing and customizable coatings, making it a popular choice for both functional and decorative applications. The cured powder coating also maintains its color and gloss over time, contributing to a long-lasting aesthetic appeal.
Environmental Friendliness: Unlike traditional liquid paints that often contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs), powder coatings are solvent-free and produce minimal to no harmful emissions during application. This makes powder coating an environmentally friendly option, aligning with contemporary sustainability practices.
Cost-Effective: Powder coating is often more cost-effective than traditional painting methods in the long run. While the initial setup costs may be slightly higher, the efficiency of the application process, reduced waste, and the longevity of the finish contribute to overall cost savings over time. The need for fewer touch-ups or recoating also minimizes maintenance expenses.
Even Coating Thickness: The electrostatic application of powder ensures an even distribution of coating material across the surface. This results in a consistent thickness of the coating, eliminating issues such as drips or uneven coverage that can occur with liquid paints. The uniformity of the coating contributes to its durability and aesthetic appeal.
Resistance to Chemicals and Corrosion: Powder coatings exhibit resistance to chemicals, corrosion, and various environmental factors. This makes them suitable for applications in industries where protection against chemical exposure or corrosion is crucial, such as automotive and industrial settings.
Fast Curing Time: The curing process for powder coating is relatively quick compared to traditional paint drying times. This efficiency contributes to increased productivity in manufacturing processes, as the coated items can be handled or packaged shortly after the curing process is complete.
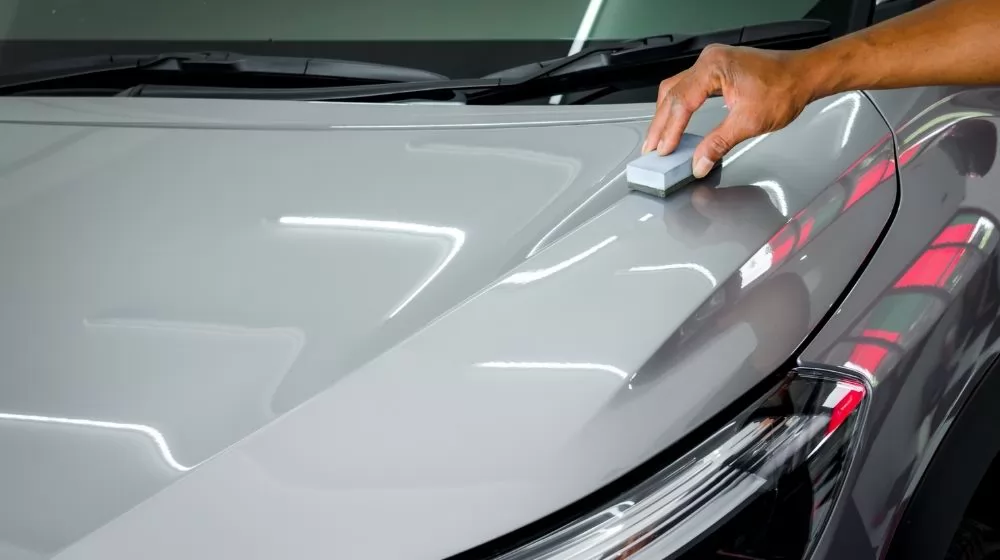

An epoxy coating is a type of protective finish that is formulated with a combination of epoxy resins and hardeners. Epoxy coatings are known for their exceptional adhesion, durability, and resistance to various environmental factors. This type of coating is commonly used for both functional and decorative purposes across a wide range of applications.
The application process of epoxy coatings involves the mixing of epoxy resin with a hardening agent. This chemical reaction creates a rigid, plastic-like material that adheres firmly to the substrate. Epoxy coatings can be applied to different surfaces, including concrete, metal, and certain plastics, providing a strong and protective layer.
Advantages of Epoxy Coating:
Exceptional Adhesion: Epoxy coatings exhibit outstanding adhesion properties, creating a strong and durable bond with various substrates. This adhesion helps prevent issues such as peeling, chipping, or delamination over time.
Chemical Resistance: Epoxy coatings are highly resistant to a wide range of chemicals, making them suitable for applications in environments where exposure to corrosive substances is a concern. This chemical resistance enhances the protective qualities of the coating.
Durability and Toughness: Epoxy coatings are known for their durability and toughness. They can withstand heavy traffic, impact, and abrasion, making them ideal for high-traffic areas and industrial settings where a robust protective layer is crucial.
Water and Moisture Resistance: Epoxy coatings form a water-resistant barrier, making them effective in environments with high humidity or occasional exposure to water. This property is particularly valuable for surfaces in areas prone to moisture, such as kitchens and bathrooms.
Decorative Options: Epoxy coatings offer a wide range of colors, textures, and patterns, providing versatility in design and aesthetics. This makes them suitable for both functional and decorative applications, allowing for customization based on the desired visual appeal.
Easy to Clean: The smooth and non-porous surface created by epoxy coatings makes them easy to clean. This feature is advantageous in environments where cleanliness and hygiene are essential, such as in commercial kitchens or healthcare facilities.
Corrosion Protection: Epoxy coatings provide effective corrosion protection for metal surfaces. This quality is particularly valuable in industries such as oil and gas, marine, and chemical processing, where metal structures are exposed to corrosive elements.
Fast Curing Time: Epoxy coatings generally have a relatively fast curing time, allowing for quick project turnaround. This efficiency is beneficial in applications where minimizing downtime is a priority.
Disadvantages of Epoxy Coating:
Surface Preparation is Critical: Achieving optimal adhesion with epoxy coatings requires thorough surface preparation. Any contaminants or inadequately prepared surfaces can compromise the coating's performance.
Sensitivity to UV Exposure: Epoxy coatings may experience color fading or yellowing when exposed to prolonged sunlight or ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This limits their suitability for outdoor applications without proper UV-resistant additives.
Application Temperature Constraints: Epoxy coatings are sensitive to temperature during application. Extreme temperatures can affect the curing process and the overall performance of the coating. Ideal application conditions need to be maintained for optimal results.
Hardness and Brittleness: While the hardness of epoxy coatings is advantageous for durability, it can also make them prone to brittleness, especially in situations where there are significant substrate movements or flexing.
Limited Thickness Application: Epoxy coatings are typically applied in thin layers. Attempts to apply a very thick layer may result in issues such as uneven curing and reduced performance.
Cost: Epoxy coatings can be relatively expensive, especially when compared to traditional paint options. The initial investment may be higher, but the long-term durability often justifies the cost.

Powder coating and epoxy coating are two distinct finishing methods with different characteristics. Here are the key differences between powder coating and epoxy coating:
1. Composition and Application:
Powder Coating: It involves applying a dry powder made of finely ground particles of pigment and resin onto a surface. The powder is electrostatically charged and adheres to the grounded object before being cured in an oven to form a solid coating.
Epoxy Coating: Epoxy coatings consist of epoxy resins and hardeners. The coating is created through a chemical reaction between the resin and hardener, forming a rigid and durable finish. Epoxy coatings are typically applied as a liquid and then cured to create a solid surface.
2. Adhesion and Durability:
Powder Coating: Offers excellent adhesion, creating a uniform and durable finish. It is resistant to chipping, scratching, and fading.
Epoxy Coating: Known for exceptional adhesion, providing a strong bond to various substrates. Epoxy coatings are highly durable and can withstand abrasion, impact, and chemical exposure.
3. Chemical Resistance:
Powder Coating: Provides good chemical resistance, but specific formulations may vary in their resistance to certain chemicals.
Epoxy Coating: Exhibits high resistance to a wide range of chemicals, making it suitable for applications in environments with corrosive substances.
4. Application Flexibility:
Powder Coating: Offers versatility in terms of color and texture, allowing for customization in design. It is commonly used for decorative as well as functional purposes.
Epoxy Coating: While available in various colors, epoxy coatings may have limitations in terms of texture compared to powder coatings. They are often chosen for their protective qualities in addition to aesthetics.
5. UV Stability:
Powder Coating: Generally exhibits good UV stability, making it suitable for outdoor applications without significant color fading or degradation.
Epoxy Coating: May experience color fading or yellowing when exposed to prolonged sunlight or UV radiation. UV-resistant additives can be incorporated to mitigate this effect.
6. Application Process:
Powder Coating: Involves a multi-step process, including electrostatic application of the powder, curing in an oven, and cooling. The process is efficient and minimizes waste.
Epoxy Coating: Requires mixing epoxy resin with a hardening agent before application. The curing process is typically achieved through chemical reaction, and curing times may vary based on the specific formulation.
7. Thickness and Flexibility:
Powder Coating: Provides a consistent and even coating thickness, but applications are generally in thin layers.
Epoxy Coating: Can be applied in thicker layers, and its flexibility depends on the specific formulation. However, epoxy coatings may become brittle in certain conditions.
Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate coating method based on the specific requirements of a project, considering factors such as environmental conditions, desired finish, and the intended use of the coated object.
Choosing between powder coating and epoxy coating depends on various factors, including the specific application requirements, the nature of the substrate, desired finish, and environmental considerations. Here are key considerations to help guide your decision:
1. Purpose of Coating:
Powder Coating: Ideal for applications where a durable, decorative finish is required. It is versatile, offering a wide range of color and texture options, making it suitable for both functional and aesthetically pleasing surfaces.
Epoxy Coating: Preferable when exceptional adhesion, chemical resistance, and durability are paramount. Epoxy coatings are often chosen for industrial and heavy-duty applications where protection against corrosion and harsh chemicals is critical.
2. Substrate Material:
Powder Coating: Well-suited for a variety of substrates, including metal, plastic, and certain types of wood. The electrostatic application ensures good adhesion to various materials.
Epoxy Coating: Effective on metals, concrete, and some plastics. The chemical bonding during the curing process enhances adhesion, making it a suitable choice for specific substrate materials.
3. Environmental Conditions:
Powder Coating: Performs well in outdoor environments, as it exhibits good UV stability and resistance to weathering. Suitable for applications exposed to sunlight and varying weather conditions.
Epoxy Coating: Resistant to chemicals and provides excellent protection against corrosion, making it suitable for environments with exposure to harsh chemicals and industrial settings.
4. Aesthetics and Design:
Powder Coating: Offers a wide range of color options and can be applied with various textures and finishes. Ideal for projects where visual appeal and customization are essential.
Epoxy Coating: While available in different colors, the design options may be more limited compared to powder coatings. Often chosen for its protective qualities rather than intricate design features.
5. Application Process:
Powder Coating: Involves an efficient and relatively straightforward process, making it suitable for high-volume production. The absence of solvents contributes to environmental friendliness.
Epoxy Coating: Requires careful mixing of epoxy resin and hardener before application. Curing times can vary, and the process may involve multiple steps, depending on the formulation.
6. Cost Considerations:
Powder Coating: While initial setup costs may be higher, the long-term durability and reduced maintenance costs often justify the investment.
Epoxy Coating: May have lower initial costs, but the overall expense can vary based on the specific requirements of the project and the chosen epoxy formulation.
7. UV Sensitivity:
Powder Coating: Generally exhibits good UV stability, making it suitable for outdoor applications without significant color degradation.
Epoxy Coating: May experience color fading or yellowing when exposed to prolonged sunlight. Incorporating UV-resistant additives can mitigate this effect.

The choice of powder coating and epoxy coating depends on specific project requirements, from aesthetic preferences to functional needs. While powder coatings excel at providing a versatile and visually appealing finish, epoxy coatings stand out for their strong protective qualities, making them indispensable in industrial settings. If you have any questions about the choice between the two, please contact Wintoly to answer your questions. Please feel free to contact us at any time!
1. What is powder coating?
2. What are the benefits of using powder coating?
3. What industries commonly utilize powder coating?
4. How do I choose a reliable powder coating supplier?
5. What types of powder coatings are available?
6. What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for powder coatings?
7. Can I request custom colors or formulations?
8. How do I ensure quality control when ordering powder coatings?
9. What are the typical curing requirements for powder coatings?
10. What are the payment terms typically offered by powder coating suppliers?
11. How can I request samples of powder coatings?
12. What should I consider when applying powder coatings?
When selecting a powder coating supplier, it’s essential to evaluate their product offerings, quality assurance processes, and customer service. Doing thorough research can help you find a supplier that meets your specific needs effectively.
Read More:
Origins and Values of Leading Powder Coating Brands: Tiger Drylac and Asian Paints
Top 10 Powder Coating Companies in South Africa (Updated 2025)

 terrychen@wintoly.com
terrychen@wintoly.com
.png) 0086-757-85407388
0086-757-85407388
 6 Chaoyang Rd., National Demonstration Eco-industrialzone, Nanhai, Foshan,Guangdong,China
6 Chaoyang Rd., National Demonstration Eco-industrialzone, Nanhai, Foshan,Guangdong,China

.png)
