.png)

.png)
.png)


-
.png) 0086-757-85407388
0086-757-85407388 -

-
 terrychen@wintoly.com
terrychen@wintoly.com


.png)

.png)
.png)


.png)




In the intricate world of industrial finishes, the debate between Powder Coating and E-Coating often takes center stage. Each method has its unique benefits, making the choice a crucial one for businesses aiming for quality and durability. Whether you're a manufacturer, supplier, or a business owner, understanding the subtle nuances between these two can significantly impact the final product's look, feel, and longevity. Let's embark on this comprehensive guide to demystify these techniques and help you make an informed decision.
In the vast and evolving world of coatings, the importance of understanding the basics cannot be stressed enough. When it comes to industrial manufacturing, the choice of coating technique plays a pivotal role in determining product quality, longevity, and aesthetics. Essentially, coating processes are employed to offer protection against environmental factors, enhance appearance, and improve performance. But, how do you determine which coating technique is right for your product? Let's delve into a concise overview of the principal players in this arena: Powder Coating and E-Coating (Electrophoretic Coating).
At its core, Powder Coating is a dry finishing process. It's been a popular choice for industries for decades due to its efficiency, environmental-friendly nature, and high-quality finish. Powder coatings are applied electrostatically and then cured under heat, resulting in a protective and decorative finish that is both resilient and versatile.
On the other hand, E-Coating or Electrophoretic Coating, is a method that uses an electrical charge to deposit paint onto a workpiece submerged in a bath. It's known for its uniform application, even on complex geometric surfaces. The method ensures a consistent, corrosion-resistant coating which makes it a prime choice for several automotive and industrial applications.
Both these techniques have their merits, and their utilization largely depends on the specific requirements of a project. Whether it's about achieving a certain aesthetic appeal or ensuring long-lasting protection against wear and tear, the coating world has a solution. In the upcoming sections, we will delve deeper into the intricacies and comparisons between these two prominent techniques, enabling manufacturers to make informed decisions.
Powder Coating is one of the most widely adopted finishing techniques in various industries due to its durability, eco-friendliness, and versatility. But what exactly is it, and how does it stand apart from other techniques? Let's uncover the essence of this process.
At a high level, powder coating is precisely what it sounds like: a coating process that utilizes a free-flowing, dry powder instead of a liquid solvent. The main distinction between a conventional liquid paint and a powder coating is the absence of a solvent in powder coating, which is needed to keep the binder and filler parts in a liquid suspension form.
The process begins with the preparation of the surface that is to be coated. Any impurities, oil, or dirt is meticulously cleaned off, ensuring an optimal environment for the coating. Once prepared, the powder, which is composed of finely ground particles of resin and pigment, is applied electrostatically. This means the powder particles are given a negative charge while the object to be coated is grounded. This causes an attraction, ensuring the powder adheres to the surface effectively.
After the application, the object enters a curing oven. Here, the powder melts and forms a chemical bond with the object, resulting in a smooth, even layer. This fusion creates a hard, durable coating that is resistant to peeling, cracking, and UV rays. It's worth noting that powder coating offers a plethora of color and texture options, from high gloss and matte to textures and clear finishes.
One of the standout features of powder coating is its eco-friendliness. Since it lacks solvents, it emits fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere. Plus, any unused or oversprayed powder can be collected and reused, minimizing waste.
In summary, powder coating is a powerful, versatile, and sustainable coating solution. Its ability to provide a high-quality, durable finish, coupled with its environmentally-conscious properties, makes it a preferred choice for many manufacturers seeking excellence in both form and function.
E-Coating, which stands for Electrophoretic Coating, is a method that's rapidly gained traction in various industrial sectors due to its precision, efficiency, and even coating application. But how does it work, and what benefits does it bring to the table? Let's explore this innovative technology in detail.
E-Coating is a wet paint finishing process that uses electrical current to deposit a paint or finish onto a part or assembled product. The beauty of this method lies in its use of electrical charges, ensuring that the coating material adheres to every nook and cranny of the object being coated.
The process begins with the parts being submerged into a water-based solution containing paint particles. An electrical charge is then applied, causing the paint particles to migrate towards the object and attach themselves uniformly to its surface. Thanks to the electrophoretic movement, even the most intricate parts with recessed areas receive an even coat. Once coated, the parts are then cured in an oven, solidifying the paint and providing a robust, corrosion-resistant finish.
There are numerous advantages to the E-Coating process. First and foremost, its ability to deliver a uniform coating is unparalleled, especially when it comes to complex geometries. This results in excellent corrosion resistance and protection, making it a top choice for automotive parts, industrial machinery, and other metal products prone to wear and tear.
Furthermore, the E-Coating process is remarkably efficient. Overspray or excess paint in the bath can be recovered and reused, reducing waste and ensuring that resources are used optimally. Not to mention, the water-based nature of the process means fewer VOC emissions, marking a nod towards a more environmentally responsible coating solution.
To conclude, E-Coating technology represents a modern, efficient, and highly effective method of coating, especially for those intricate parts that require consistent coverage and protection. As industries continue to innovate and demand more from their coating processes, E-Coating is poised to be a significant player in the realm of finishes.
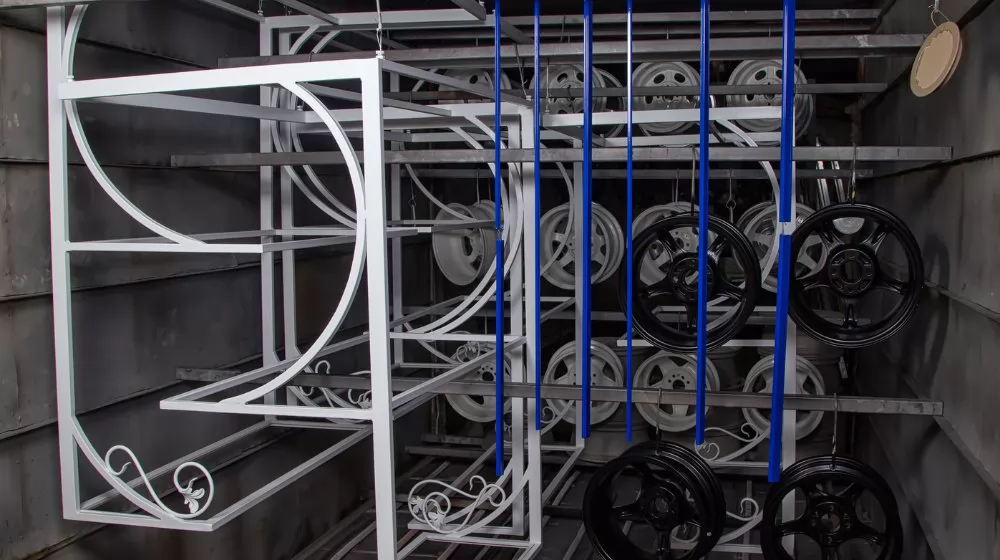
Understanding the science behind powder coating helps appreciate its efficacy and the precision with which it operates. Far more than just a finishing touch, powder coating is a symphony of chemistry, physics, and engineering, all harmonizing to produce a durable and aesthetically pleasing finish. Let's dissect the science behind this renowned technique.
1. The Powder Itself: At its heart, the powder used in this technique is a combination of polymer resin systems, pigments, leveling agents, flow modifiers, and other additives. These ingredients are melt-mixed, cooled, and then ground into a fine powder, resembling baking flour in consistency. Each ingredient serves a distinct purpose, from determining the finish and color of the coating to its durability and reaction to external factors.
2. Electrostatic Application: Physics comes into play during the application process. Using a spray gun, the powder particles are imparted a negative electric charge. The object to be coated, on the other hand, is grounded. This creates an electric attraction, pulling the charged powder particles to the object's surface. It’s this electrostatic principle that ensures an even and adhesive coverage, even on complex geometries.
3. Curing Process: After the application, the coated object is introduced to a curing oven. Here, chemistry takes center stage. The heat causes the powder particles to melt and chemically bond, forming long-chain polymers. These polymers provide the coating's characteristic durability and resilience, creating a protective barrier against environmental aggressors.
4. Environmental Benefits: From a chemical perspective, the absence of solvents in powder coatings means they emit fewer VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds) when compared to traditional liquid coatings. This not only benefits the environment but also reduces health risks for workers in the industry.
In essence, powder coating is a meticulous dance of science and technique. Its efficiency isn't just by chance; it's the result of deliberate scientific principles, expertly leveraged to produce a finish that's both beautiful and enduring. As industries continually evolve, so does the science behind them, and powder coating is no exception to this rule of progression.
Delving into the world of E-Coating brings forth a captivating interplay of chemical reactions. This immersive technique, while primarily known for its practical benefits, is rooted deeply in chemistry. Let's navigate the intricate chemical processes that make E-Coating a technological marvel in the coating industry.
1. Composition of the E-Coat Bath: The bath used in E-Coating is a water-based solution, comprising mainly of organic resins and coalescing agents. These resins can be epoxy, acrylic, or a hybrid of both. Additionally, pigments and other performance-enhancing additives are introduced, determining color, gloss, and durability of the coating. The water acts as a solvent, making it an eco-friendly option in comparison to solvent-borne coatings.
2. Electrophoretic Deposition: The name E-Coating originates from 'electrophoresis', the movement of charged particles in a fluid when subjected to an electric field. When an electric potential is applied, the charged resin particles migrate towards the oppositely charged workpiece and are deposited on its surface in a process known as "electrophoretic deposition". This ensures a uniform layering even in the most intricate parts.
3. Coagulation and Curing: Post deposition, the coated parts are heated, causing the resin particles to coagulate, fuse, and cross-link. This cross-linking is a series of chemical reactions where polymers interconnect, forming a seamless and impervious film. The end product is a resilient, chemically bonded coating, firmly adhered to the substrate, granting it resistance against corrosion, UV rays, and other environmental challenges.
4. pH and Conductivity: Two critical parameters in the E-Coating process are pH and conductivity. The pH ensures the bath's stability and performance, while conductivity affects the coating's thickness. Regular monitoring and adjustments of these parameters are crucial, establishing the desired balance and maintaining the integrity of the process.
In conclusion, the chemistry behind E-Coating is both intricate and fascinating. Its capability to provide an even, durable coating while minimizing waste and environmental impact showcases the power of leveraging chemistry for industrial advancements. As technology and chemistry continue to evolve hand-in-hand, E-Coating remains a testament to the harmonious union of science and practical application.
Both Powder Coating and E-Coating are renowned for their distinct properties and application benefits. However, at the heart of their effectiveness lies the composition of materials that make up each process. To fully appreciate their strengths and applications, it's crucial to understand the primary ingredients involved.
1. Polymer Resins: These are the primary binders in the powder mix. Common resins include epoxy, polyester, urethane, and hybrids of these. The type of resin influences durability, flexibility, and the finish's overall appearance.
2. Pigments: Responsible for the color and opacity of the coating. These can range from organic pigments, like phthalocyanines, to inorganic ones, such as titanium dioxide or iron oxide.
3. Flow Modifiers: These agents assist in achieving a smooth finish by influencing the flow characteristics of the molten powder during the curing process.
4. Curing Agents: These are reactive components that, when heated, cause the polymer resin to cross-link, forming a continuous, durable film.
1. Water-Based Resin: E-Coats utilize water as a primary solvent, with the resins being either epoxy-based or acrylic-based. These resins determine the performance properties and appearance of the e-coat.
2. Pigments: Similar to powder coatings, pigments in e-coats provide color and opacity. The selection of pigments can influence properties such as UV resistance and corrosion protection.
3. Coalescing Agents: These help in film formation during the curing process, ensuring the resin and pigments meld seamlessly.
4. Additives: These can vary depending on the desired properties of the e-coat. Common additives might include anti-foaming agents, flow enhancers, or UV stabilizers.
In summary, while both Powder Coating and E-Coating rely on resins and pigments as primary components, the differentiation lies in their application processes, curing methods, and specific ingredients tailored to their unique performance needs. An informed decision between the two hinges on understanding their compositional differences and the distinct benefits they offer.
The application processes of Powder Coating and E-Coating are distinctive, each tailored to maximize the advantages of their material compositions. Let's uncover the step-by-step workflows for both methods, laying out their intricacies and efficiencies.
1. Surface Preparation: Before applying the powder coat, the object is thoroughly cleaned to remove oils, dirt, rust, and other contaminants. Methods include chemical cleaning, abrasive blasting, or phosphating.
2. Powder Application: The powder, composed of finely ground particles of pigment and resin, is sprayed onto the surface using an electrostatic gun (or corona gun). The gun imparts a positive electric charge to the powder, which is then attracted to the grounded object, ensuring an even coat.
3. Curing: Once the object is evenly coated, it is placed in an oven where the powder particles melt and chemically react to form long polymer chains, resulting in a hard, cohesive finish.
4. Cooling and Finalizing: After curing, the object is allowed to cool, solidifying the coating. Once cooled, the object is inspected for any defects and is ready for use or further processing.
1. Pre-treatment: Similar to powder coating, the object's surface must be impeccably clean. It undergoes a series of cleaning and phosphating steps to ensure optimal adhesion.
2. E-Coat Immersion: The object is submerged into the E-coat bath, which is a water-based solution containing the necessary resins and pigments. An electric current is then passed, causing the paint particles in the bath to deposit onto the object's surface through electrophoretic deposition.
3. Rinsing: After E-coating, the object is rinsed to remove any excess paint from its surface and recessed areas.
4. Curing: The coated object is baked in an oven, causing the coating to cross-link and form a solid, durable layer.
5. Inspection and Quality Control: As with powder coating, the final E-coated object undergoes a rigorous inspection to ensure quality and uniformity.
In conclusion, while both Powder Coating and E-Coating have their unique application workflows, they converge on the shared objective of achieving a durable, high-quality finish. The choice between them largely depends on the specific requirements of the job at hand, from aesthetic desires to functional necessities.
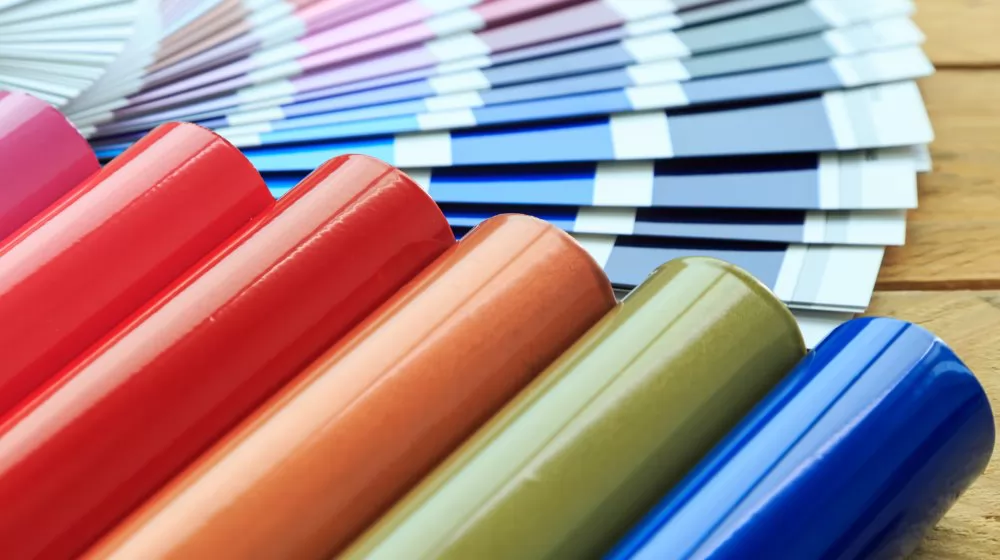

One of the most significant advantages of powder coating is its resilience. Unlike traditional liquid paints, powder coating forms a thick, adhesive finish that lasts longer and resists chipping, scratching, and other wear. This ensures that the underlying material, whether metal, plastic, or another substrate, remains protected from corrosion, wear, and exposure. Products with powder coating often enjoy a lifespan several times longer than their traditionally painted counterparts.
With an extensive range of available colors and finishes, powder coating offers unparalleled aesthetic versatility. From vibrant hues to subtle shades, matte to high gloss, and even textures, the options are nearly limitless. This breadth of choice allows manufacturers and designers the freedom to achieve the desired appearance for their products. The even application process ensures a uniform, sleek finish, enhancing the product's visual appeal.
Environmental responsibility is more than a buzzword—it's a commitment, and powder coating rises to the occasion. Unlike liquid paints that often contain solvents and release Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere, powder coatings are predominantly solvent-free. This not only reduces harmful emissions but also ensures a safer working environment. Plus, excess powder can be recovered and reused, minimizing waste and promoting a sustainable approach to finishing.
In conclusion, powder coating stands out not just for its superior finish but for its commitment to longevity, aesthetic versatility, and the environment. As industries move towards more sustainable and durable solutions, powder coating continues to set the benchmark.
While powder coating is widely recognized for its durable finish and environmental benefits, like any process, it's not without its challenges. Understanding these disadvantages is essential for manufacturers to make informed choices based on their specific needs and project constraints.
Powder coating, due to its application method, often results in a thicker coating compared to traditional liquid paints. While this can be an advantage in terms of durability, it can also be a limitation. Achieving thin coatings with powder can be challenging, and over-application can result in runs, sags, or other surface imperfections. Industries or applications that demand ultra-thin coatings may find powder coating less than ideal.
The electrostatic nature of powder coating means that it is inherently drawn to the most exposed areas of a part. This phenomenon, known as the Faraday Cage Effect, can make it challenging to get consistent coverage in recessed areas or intricate designs. As a result, objects with complex geometries or deep recesses may not be uniformly coated, leading to potential performance issues or aesthetic inconsistencies.
Setting up a powder coating line can be capital intensive. The requirement for specialized equipment like spray booths, electrostatic guns, and curing ovens can lead to significant initial expenses. While the long-term benefits in terms of durability, reduced waste, and environmental impact can justify the cost, small businesses or those with tight budgets might find the initial investment challenging to bear.
In conclusion, while powder coating offers numerous advantages in terms of durability, environmental impact, and finish quality, it's crucial for businesses to weigh these benefits against the potential challenges. As always, the decision should be based on the specific requirements of the project and the longer-term objectives of the business.
E-Coating, or electrophoretic coating, has steadily gained prominence in various industries due to its array of benefits. While every coating process has its own strengths and weaknesses, E-Coating stands out in several crucial areas that make it a preferred choice for many manufacturers.
One of the standout features of E-Coating is its ability to ensure a consistent, uniform layer of coating across the entire object. Thanks to the electrophoretic deposition process, the paint particles are drawn to the substrate uniformly, regardless of its shape or size. This means even complex objects with nooks, crannies, and recesses receive an even coat, reducing the risk of patchiness or areas of under-coating.
Corrosion resistance is paramount in many industries, especially automotive and marine applications. E-Coating shines in this aspect. When properly applied and cured, the coating forms a barrier that effectively prevents moisture, salts, and other corrosive agents from reaching the underlying substrate. This translates to longer-lasting protection and extended product lifespan, which is crucial for parts exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
On a large scale, E-Coating can be incredibly cost-effective. The immersion process used in E-Coating ensures that almost every part of the paint is utilized, minimizing waste. Moreover, the ability to coat many parts simultaneously, combined with the rapid curing times, means that large batches can be processed efficiently. For manufacturers that handle bulk orders or continuous production lines, this can result in significant cost savings over time.
In conclusion, E-Coating offers a compelling blend of uniformity, protection, and cost-effectiveness that positions it as a top choice for many coating needs. As with any process, it's essential to match the method to the specific requirements of the project, but for many applications, E-Coating emerges as a clear frontrunner.
E-Coating, while notable for its advantages, does come with its own set of challenges. Recognizing these drawbacks is crucial for manufacturers and businesses to make well-informed decisions tailored to their unique needs.
One of the primary drawbacks of the E-Coating process is the limited range of colors available. Unlike other methods that allow for extensive customization, E-Coating typically offers a narrower selection. This limitation can be a deal-breaker for industries or projects that require vibrant or highly specific colors. While advancements are being made to broaden the color palette, it's still a constraining factor for many applications.
E-Coating requires a curing process that often involves high temperatures for extended periods. This can be energy-intensive, especially when compared to other finishing processes. Businesses with a strong emphasis on sustainability or those operating in areas with high energy costs might find this aspect of E-Coating challenging.
While E-Coating is lauded for its efficient use of material, there are still environmental considerations to keep in mind. The process involves solvents and chemicals, which, if not managed correctly, can pose environmental risks. Proper waste management and adherence to environmental regulations are imperative to ensure the process remains as green as possible.
In summary, while E-Coating offers numerous advantages in terms of uniformity, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness, it's essential for businesses to be aware of its limitations. As always, the right coating solution should be tailored to the specific requirements and constraints of each project.
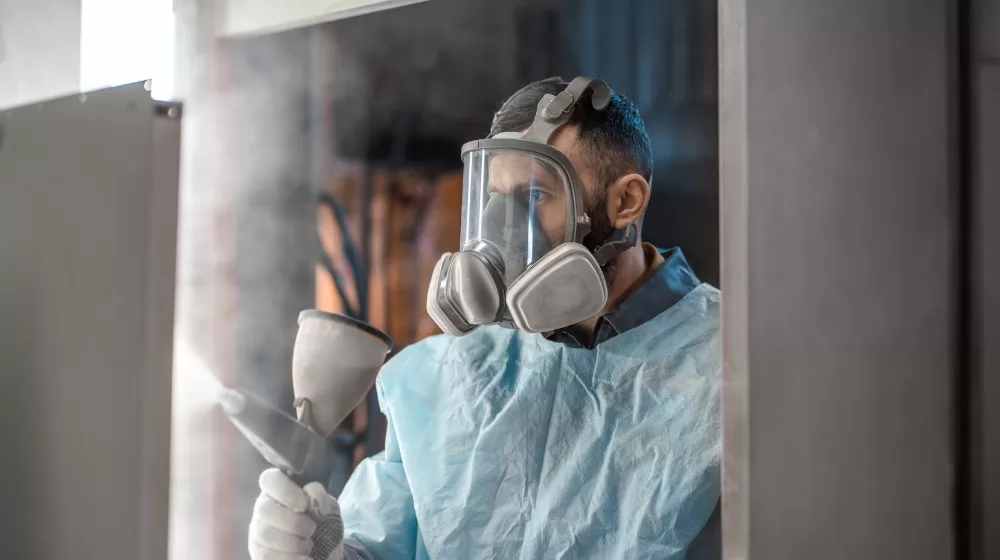

When it comes to the finishing touches on products, the aesthetic appeal is often as important as the functional protection offered by coatings. Both Powder Coating and E-Coating have their unique visual characteristics that can impact the final look of a product. Let's dissect the visual outcomes of both methods:
Powder Coating is renowned for its rich, vibrant, and durable finishes. Here's what you can expect from this method:
E-Coating, while primarily chosen for its protection, doesn't fall short in the aesthetics department either. Here's what this process offers:
In conclusion, the choice between Powder Coating and E-Coating doesn't just come down to functional needs; aesthetic considerations play a pivotal role too. The right pick will depend on the visual outcome the manufacturer or designer envisions for the final product.
Cost plays a pivotal role when manufacturers decide on a coating technique. Both Powder Coating and E-Coating come with their own sets of economic factors to consider. While each has its advantages, the overall return on investment (ROI) might differ based on the scale, scope, and specific requirements of the project. Let's unpack the cost implications:
Powder Coating has its own set of cost parameters:
When considering E-Coating, several economic facets come into play:
To wrap it up, while both Powder Coating and E-Coating come with their distinct cost structures, the decision largely hinges on the specific requirements of the project, the scale of the operation, and long-term ROI considerations. It's crucial for businesses to factor in both initial and operational costs to make an informed choice.
In the current age of environmental consciousness, businesses are not just evaluated by the quality of their products but also by the sustainability of their processes. Both Powder Coating and E-Coating have ecological implications that need careful examination:
Powder Coating offers a range of environmental benefits:
E-Coating, while efficient, has certain environmental aspects to consider:
To sum it up, while Powder Coating offers an edge in terms of VOC emissions and waste reduction, E-Coating demands rigorous water treatment and energy considerations. Manufacturers need to weigh these factors, alongside performance requirements, to make an environmentally responsible choice.
The choice between Powder Coating and E-Coating often hinges on industry-specific needs. Here's an exploration into which sectors predominantly use these methods and notable examples of their application:
Powder Coating is a versatile process finding its home in diverse industries:
Case Study Highlight: A leading automobile manufacturer shifted to powder coating for its car rims, resulting in reduced warranty claims related to chipping and increased customer satisfaction.
E-Coating, known for its uniform finish, is prevalent in the following sectors:
Case Study Highlight: An international aerospace company incorporated e-coating for its aircraft landing gears, significantly extending their operational lifespan and reducing maintenance costs.
The battle between Powder Coating and E-Coating isn't about superiority but suitability. The choice boils down to the specific needs of a project. Here’s a primer on the evaluations and factors that influence this decision:
Before diving into a coating process, it's imperative to clarify the project’s demands:
Several factors play a part in swaying the decision towards one method over the other:
In essence, the decision to opt for Powder Coating or E-Coating is multifaceted. A comprehensive assessment, considering both the project's demands and overarching operational considerations, will guide businesses to the right choice, ensuring both quality and efficiency.
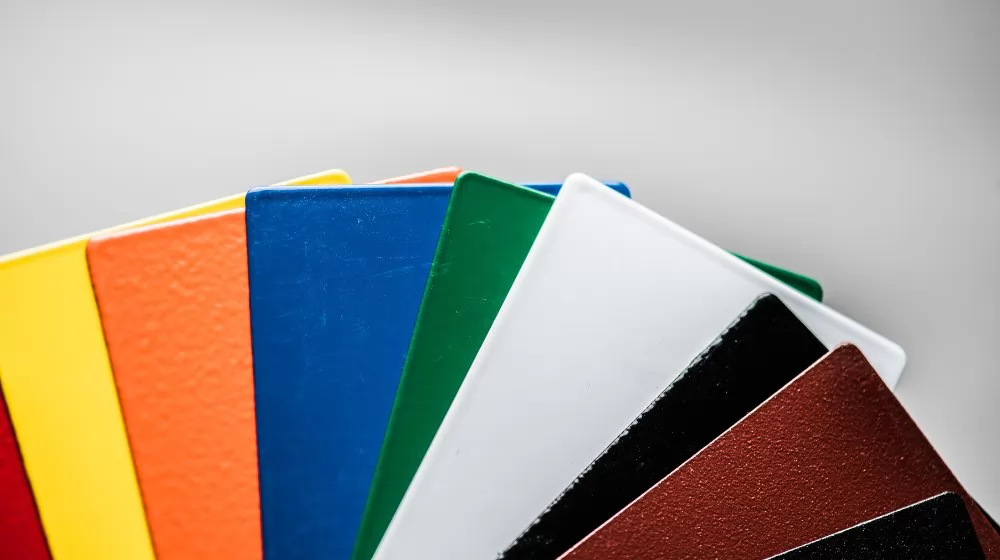

In today's competitive market, the finish of your product isn’t just about aesthetics—it’s about durability, environmental considerations, and reflecting the high standards of your brand. Powder coating, with its myriad benefits, stands out as the go-to choice for many businesses. If you're considering integrating this technology, choosing the right partner is essential.
Here's why Wintoly should be on your radar:
Taking your product to the next level requires meticulous attention to detail, expertise, and the right partner. With Wintoly's impeccable track record in powder coating, your project is in capable hands. Reach out, and let's add that exceptional finish to your next project.
Read More:

 terrychen@wintoly.com
terrychen@wintoly.com
.png) 0086-757-85407388
0086-757-85407388
 6 Chaoyang Rd., National Demonstration Eco-industrialzone, Nanhai, Foshan,Guangdong,China
6 Chaoyang Rd., National Demonstration Eco-industrialzone, Nanhai, Foshan,Guangdong,China

.png)
